Note
For a better understand the mechanism of retrieving metadata through the Z39.50 extension, the information from the chapter about importing metadata in the bibliographic description editor will be useful, as well as acquaintance with the Z39.50 protocol.
Note
The programming library for that extension is dlibra-app-extension-sl-z3950.
Many library systems make metadata available through the Z39.50 protocol. The Editor Application extension discussed here makes it possible to retrieve metadata from systems which make them available through the Z39.50 protocol. The Z39.50 protocol is a very complex standard for sending metadata in various formats. The extension in question only allows metadata retrieval from the MARC 21 communication format (specifically, the USMARC format). The metadata retrieved with the use of that extension can be imported by means of an extension for importing files in the MARC format.
In order to retrieve metadata with the use of the Z39.50 protocol:
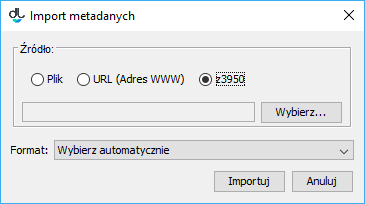
In the metadata editor, in the “Metadata import/export” panel, click the “Import...” button. The metadata import window will appear (see the image below). The metadata import window contains the Z39.50 option which determines the use of the Z39.50 extension for selecting the file with the metadata to be imported.
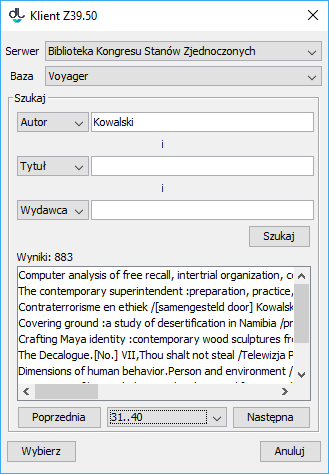
Okno importu metadanychIn order to select the metadata to be imported, click the “Select...” button. The metadata search window will be displayed (see the image below). In that window, the user can select the server and the base to which search queries will be directed. A search query is built on the basis of three values/phrases which are entered by a user in fields on the “Search” panel. The attribute search can be adjusted by a user by selecting appropriate attributes from the expandable lists. In the image below, the attributes selected for the search are “Author”, “Title”, and “Publisher”. In order to start the search, click the “Search” button. Once the search has finished, the results can be viewed with the use of the “Previous” and “Next” buttons, which lead, respectively, to the previous or next page of the search results. The editor can also select a particular page from the search results directly, by means of the expandable list located between the “Previous” and “Next” buttons.
Okno wyszukiwania metadanych poprzez protokół Z39.50- In order to select the metadata, select the appropriate position on the list of search results and click the “Select” button. The file will be downloaded to the local computer drive. The Z39.50 search window will be closed. In the metadata import window, the path to the downloaded metadata file will be entered (automatically). The next steps should be taken in accordance with the instructions in the section about importing metadata (in the simplest cases, one just has to click the “Import” button in the metadata import window).
The Z39.50 extension can be adjusted to the needs of a particular installation by means of an appropriate configuration. The configuration of the extension is located in the configuration file, z3950_servers.xml. That file defines, among other things, the servers and databases in which the editor will be able to find metadata, the attributes for searching a particular server, and the logical connective for connecting queries from particular search fields. The default configuration file of the Z39.50 extension is shown below.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <servers> <server> <name>Library of Congress</name> <name lang="en">Library of Congress</name> <name lang="pl">Biblioteka Kongresu Stanów Zjednoczonych</name> <host>z3950.loc.gov</host> <port>7090</port> <databases> <database>Voyager</database> </databases> <recordencoding>MARC-8</recordencoding> <queries> <attrset>@attrset bib-1</attrset> <operator>@and</operator> <query> <name>Author</name> <name lang="pl">Autor</name> <name lang="en">Author</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=1003 $1</searchquery> </query> <query> <name>Title</name> <name lang="pl">Tytuł</name> <name lang="en">Title</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=4 $1</searchquery> </query> <query> <name>Publisher</name> <name lang="pl">Wydawca</name> <name lang="en">Publisher</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=1018 $1</searchquery> </query> <query> <name>Everywhere</name> <name lang="pl">Wszędzie</name> <name lang="en">Everywhere</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=1035 $1</searchquery> </query> </queries> </server> </servers>
Plik konfiguracyjny zapisany jest w formacie XML. Głównym węzłem w pliku jest <servers>, w którym znajdują się definicje serwerów Z39.50 (liczba serwerów nie jest ograniczona). Każdy serwer zdefiniowany jest w ramach znacznika <server> w którym znajdować się powinny następujące informacje w poszczególnych znacznikach:
<name>- jest to nazwa serwera wyświetlana redaktorowi w oknie wyszukiwania metadanych. Nazwę można wprowadzić dla konkretnego języka poprzez zastosowanie w znaczniku<name>atrybutulang. Wartością atrybutulangpowinien być dwuliterowy symbol języka (zgodnie ze standardem ISO 639), w którym specyfikowana jest nazwa serwera. Domyślna nazwa serwera określana jest w znaczniku<name>, który nie posiada atrybutulang. Proszę zauważyć, że poszczególne nazwy definiowane są w odrębnych znacznikach<name>.<host>- jest to adres internetowy serwera Z39.50 (adres IP lub adres domenowy).<port>- jest to port serwera Z39.50.<user>- nazwa użytkownika, jeśli serwer wymaga uwierzytelniania<password>- hasło użytkownika, jeśli serwer wymaga go do uwierzytelniania<databases>- w tym znaczniku znajdują się nazwy baz danych, które redaktor może przeszukiwać. Poszczególne nazwy powinny być wprowadzane w znacznikach<database>.<recordencoding>- jest to kodowanie rekordów metadanych, które udostępnia definiowany serwer Z39.50.<queryencoding>- jest to kodowanie, w jakim mają być wysyłane frazy w zapytaniach do serwera. Znacznik jest opcjonalny, domyślnie stosowane jest kodowanie US-ANSI.<setname>- jest to nazwa zbioru właściwości, który ma być zwrócony dla każdego znalezionego elementu. Jest to znacznik opcjonalny, domyślnie przyjmuje wartośćF(od full - pełen zbiór). Często jest też używana wartośćB(od brief - skrócone). Jeśli nazwa zbioru nie jest poprawnie ustawiona, pobieranie danych zakończy się błędem, a w konsoli Java pojawi się komunikat:Z3950SearchTask - Non surrogate diagnostics [25].<queries>- jest to węzeł w którym definiuje się informacje związane z panelem wyszukiwawczym. Wszystkie wartości, które rozpoczynają się od znaku@związane są z językiem zapytań stosowanym w bibliotece JZKit 2 (http://jzkit.org/). I tak:<attrset>- określa zestaw atrybutów jaki jest używany do wyszukiwania.<operator>- określa operator logiczny, który będzie używany do łączenia specyfikowanych wartości/fraz w polach wyszukiwawczych.<query>- specyfikuje nazwę atrybutu po którym możliwe będzie wyszukiwanie oraz zapytanie wyszukiwawcze związane z tym atrybutem. Nazwa atrybutu podobnie jak w przypadku nazwy serwera może być wprowadzona w wielu językach (użycie atrybutulang). Domyślna nazwa atrybutu to wartość zawarta w znaczniku<name>, który nie posiada atrybutu lang. Zapytanie wyszukiwawcze specyfikuje się w znaczniku<searchquery>, gdzie w miejsce znacznika$1wstawiana jest wartość z odpowiedniego pola wyszukiwawczego.
Aby zmienić konfigurację rozszerzenia Z39.50 należy postępować zgodnie z informacjami zawartymi w sekcji konfiguracja aplikacji.