...
The Extensions of the Reader Application
| Table of Content Zone | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||
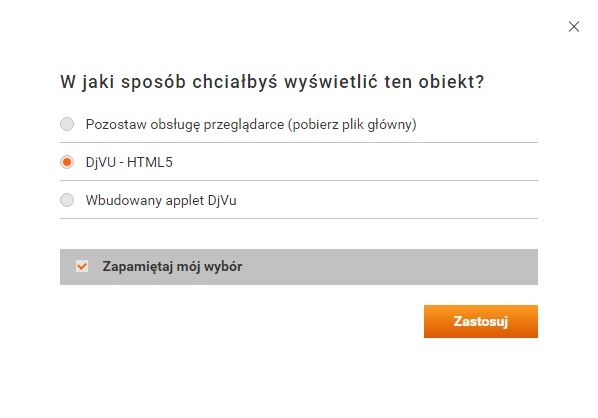
The Extension Mechanism of the Reader Application of the dLibra SystemSince version Mechanizm rozszerzeń aplikacji czytelnika systemu dLibraOd wersji 5.0 systemu dLibra wprowadzono mechanizm rozszerzeń prezentacji treści publikacji. Niektóre formaty dokumentów wymagają od użytkownika instalacji odpowiednich rozszerzeń dla przeglądarki np. format DjVu. W aplikacji czytelnika systemu dLibra istnieją mechanizmy pozwalające na prezentacje niektórych typów plików w formie przyjaznej dla użytkowników. Mechanizmy te bazują na oprogramowaniu kompatybilnym z HTML oraz na domyślnych rozwiązaniach przeglądarek internetowych. Aplikacja czytelnika na podstawie typu i nazwy głównego pliku publikacji określa czy dostępne są rozszerzenia sposobu prezentacji dla danej publikacji. Jeżeli tak, przed wyświetleniem treści prezentuje użytkownikowi listę dostępnych rozszerzeń (por. rysunek). Użytkownik może skorzystać z odtwarzacza wbudowanego w dLibrę lub pozostawić obsługę przeglądarce (jeżeli posiada już zainstalowaną wtyczkę). Budowa i sposób działania rozszerzeń prezentacji treści., the dLibra system has had an extension mechanism for presenting publication content. For some document formats (for example, for the DjVu format), the reader must install appropriate browser extensions. In the Reader Application of the dLibra system, there are mechanisms for presenting some file types in a user-friendly form. The mechanisms are based on software compatible with HTML and on the default solutions of Internet browsers. . On the basis of the type and name of the main publication file, the Reader Application determines if extensions for the manner of content presentation are available for the given publication. If they are, the application displays the list of the available extensions to the reader (see the figure above), before displaying the content. The user can use the player built into the dLibra system or leave the handling to the browser (if the plugin is already installed). The Structure and Operation of Content Presentation ExtensionsEvery extension used for presenting content consists of two parts: files visible through the WWW, for example, JavaScript files or CSS sheets; those files are in the Każde z rozszerzeń używanych do prezentacji treści składa się z dwóch części. Plików widocznych przez WWW np. skryptów JavaScipt, arkuszy CSS. Pliki te znajdują się w katalogu dlibra-webapp-5.0/formats/nazwa-rozszerzenia. Plików z konfiguracją rozszerzeń np. ustawienia związane z tym jakie formaty dane rozszerzenie jest w stanie wyświetlać, szablony VTL używane do generowania kodu HTML rozszerzenia, tekst wyświetlanego ostrzeżenia. Pliki te znajdują się w katalogu extension-name catalog; and files with extension configuration, for example, settings of the data formats which the given extension can display, VTL templates for generating HTML code, or a warning text; those files are in the dlibra-webapp/WEB-INF/formats/nazwaextension-rozszerzenia. Below, we describe the extension used for presenting objects in the Zoomify format. It consists of the following files:
Every content presentation extension must contain the five files listed above. The part visible from the WWW is optional. The settings.xml file contains the most important settings related to the functioning of the extension, such asPlik settings.xml zwiera najważniejsze ustawienia związane z działaniem rozszerzenia, są to między innymi:
W momencie gdy użytkownik wybierze rozszerzenie jakiego chce użyć do prezentacji treści, aplikacja czytelnika generuje ostrzeżenie dotyczące formatu - renderowana jest zawartość pliku message.vm przy użyciu etykiet tekstowych z plików messages_pl.xml i messages_en.xml. Następnie użytkownik przechodzi do treści, aplikacja czytelnika wyświetla wyrenderowany szablon content.vm. W szablonie tym określone są odwołania do widocznych od strony WWW elementów rozszerzenia formatu prezentacji treści oraz do pliku z treścią publikacji. Z poziomu szablonu content.vm tworzący rozszerzenia prezentacji treści ma do dyspozycji dwie zmienne:
When the user has chosen an extension for presenting content, the Reader Extension generates a warning which pertains to* the format – the content of the message.vm file is rendered with the use of the text labels from the messages_pl.xml and messages_en.xml files. Next, the user goes to the content, and the Reader Application displays the rendered content.vm template. In that template, references to a) the elements of the extension for the manner of content presentation which are visible from the WWW and b) the file with the publication content. From the level of the content.vm template, two variables are available for the person creating extensions for presenting content:
In the case of the presented extension, zoomify, the page rendered while the publication content is being displayed contains the calling of the zoomifyViewer.swf script, where the arguments include the path to the main file of the publication. The box below contains the content of the content.vm template for the djvu_htm!5 extensionW przypadku prezentowanego rozszerzenia zoomify strona wyrenderowana podczas wyświetlania treści publikacji zawiera wywołanie skryptu zoomifyViewer.swf gdzie w argumentach podawana jest ścieżka do pliku głównego publikacji. Poniżej zawartość szablonu content.vm dla rozszerzenia djvu_html5:
Domyślny sposób prezentacji treściThe Default Manner of Content PresentationThere are three files W katalogu dlibra-webapp/WEB-INF/formats znajdują się trzy pliki (message_pl.xml, message_en.xml i settings.xml) jest to konfiguracja domyślnej obsługi prezentacji formatów. Wszelkie zmiany w tych plikach mogą spowodować, że aplikacja czytelnika nie będzie działać poprawnie.in the dlibra-webapp/WEB-INF/formats catalog. That is the configuration of the default handling of the manner of content presentation. Any changes in those files may prevent the Reader Application from functioning correctly |