...
In order to retrieve metadata with the use of the Z39.50 protocol:
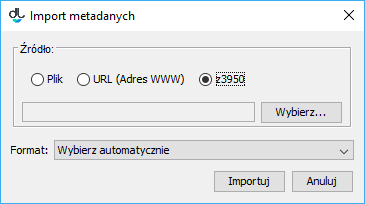
W edytorze metadanych na panelu Import/Eksport metadanych wybrać przycisk Importuj..., który wyświetli okno importu metadanych (rysunek poniżej). Na oknie importu metadanych znajduje się opcja Z39.50, którą należy wybrać. Opcja ta determinuje wykorzystanie rozszerzenia Z39.50 w celu wyboru pliku metadanych do zaimportowaniaIn the metadata editor, in the “Metadata import/export” panel, click the “Import...” button. The metadata import window will appear (see the image below). The metadata import window contains the Z39.50 option which determines the use of the Z39.50 extension for selecting the file with the metadata to be imported.
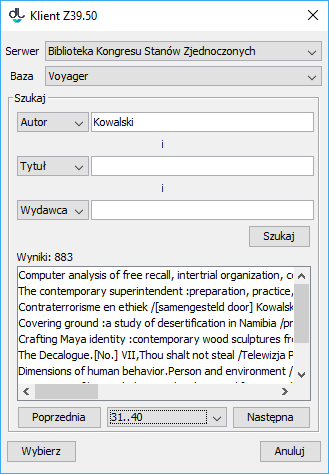
Anchor metadataImportDialog metadataImportDialog labelimg Okno importu metadanych Okno importu metadanych Aby wybrać metadane, które mają być zaimportowane należy wybrać przycisk WybierzIn order to select the metadata to be imported, click the “Select.... Pojawi się okno wyszukiwania metadanych (rysunek poniżej). W oknie tym użytkownik może wybrać serwer oraz bazę do której będą skierowane zapytania wyszukiwawcze. Zapytanie wyszukiwawcze budowane jest na podstawie trzech wartości/fraz, które wprowadzane są przez użytkownika do pól znajdujących się na panelu Szukaj. To jakie atrybuty będą przeszukiwane może być dostosowane przez użytkownika poprzez wybór odpowiedniego atrybutu z listy rozwijanej. Na przedstawionym rysunku ( Rysunek B.2.) wybrane do wyszukiwania atrybuty to autor, tytuł oraz wydawca. Aby rozpocząć wyszukiwanie należy wybrać przycisk Szukaj. Po zakończeniu procesu wyszukiwania możliwe jest przeglądanie wyników przy użyciu przycisków Poprzednia i Następna, które przechodzą odpowiednio do poprzedniej lub następnej strony wyników wyszukiwania. Redaktor może również wybrać bezpośrednio określoną stronę wyników wyszukiwania używając listy rozwijanej, która znajduje się pomiędzy przyciskami Poprzednia i Następna” button. The metadata search window will be displayed (see the image below). In that window, the user can select the server and the base to which search queries will be directed. A search query is built on the basis of three values/phrases which are entered by a user in fields on the “Search” panel. The attribute search can be adjusted by a user by selecting appropriate attributes from the expandable lists. In the image below, the attributes selected for the search are “Author”, “Title”, and “Publisher”. In order to start the search, click the “Search” button. Once the search has finished, the results can be viewed with the use of the “Previous” and “Next” buttons, which lead, respectively, to the previous or next page of the search results. The editor can also select a particular page from the search results directly, by means of the expandable list located between the “Previous” and “Next” buttons.
Anchor searchZ3950Dialog searchZ3950Dialog labelimg Okno wyszukiwania metadanych poprzez protokół Z39.50 Okno wyszukiwania metadanych poprzez protokół Z39.50 - Aby wybrać metadane należy zaznaczyć konkretną pozycję na liście wyników wyszukiwania a następnie wybrać przycisk Wybierz. Plik zostanie pobrany na lokalny dysk komputera, okno wyszukiwania Z39.50 zostanie zamknięte, a w oknie importu metadanych zostanie automatycznie wprowadzona ścieżka do pobranego pliku metadanych. Kolejne kroki należy wykonać zgodnie z informacjami zawartymi w sekcji import metadanych (w najprostszym przypadku wystarczy wybrać przycisk Importuj na oknie importu metadanych).
- In order to select the metadata, select the appropriate item on the list of search results and click the “Select” button. The file will be downloaded to the local computer drive. The Z39.50 search window will be closed. In the metadata import window, the path to the downloaded metadata file will be entered (automatically). The next steps should be taken in accordance with the instructions in the section about importing metadata (in the simplest cases, one just has to click the “Import” button in the metadata import window).
The Z39.50 extension can be adjusted to the needs of a particular installation by means of an appropriate configuration. The configuration of the extension is located in the configuration file, z3950_servers.xml. That file defines, among other things, the servers and databases in which the editor will be able to find metadata, the attributes for searching a particular server, and the logical connective for connecting queries from particular search fields. The default configuration file of the Z39.50 extension is shown belowRozszerzenie Z39.50 może być dostosowane do potrzeb konkretnej instalacji poprzez odpowiednią jego konfigurację. Konfiguracja rozszerzenia znajduje się w pliku konfiguracyjnym z3950_servers.xml. Plik ten definiuje m. in. serwery oraz bazy danych w których redaktor będzie mógł wyszukiwać metadane, atrybuty po jakich redaktor będzie mógł przeszukiwać konkretny serwer oraz operator logiczny jaki będzie użyty do połączenia zapytań z poszczególnych pól wyszukiwawczych. Poniżej przedstawiono domyślny plik konfiguracyjny rozszerzenia Z39.50.
| Code Block | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <servers> <server> <name>Library of Congress</name> <name lang="en">Library of Congress</name> <name lang="pl">Biblioteka Kongresu Stanów Zjednoczonych</name> <host>z3950.loc.gov</host> <port>7090</port> <databases> <database>Voyager</database> </databases> <recordencoding>MARC-8</recordencoding> <queries> <attrset>@attrset bib-1</attrset> <operator>@and</operator> <query> <name>Author</name> <name lang="pl">Autor</name> <name lang="en">Author</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=1003 $1</searchquery> </query> <query> <name>Title</name> <name lang="pl">Tytuł</name> <name lang="en">Title</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=4 $1</searchquery> </query> <query> <name>Publisher</name> <name lang="pl">Wydawca</name> <name lang="en">Publisher</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=1018 $1</searchquery> </query> <query> <name>Everywhere</name> <name lang="pl">Wszędzie</name> <name lang="en">Everywhere</name> <searchquery>@attr 1=1035 $1</searchquery> </query> </queries> </server> </servers> |
Plik konfiguracyjny zapisany jest w formacie XML. Głównym węzłem w pliku jest <servers>, w którym znajdują się definicje serwerów Z39.50 (liczba serwerów nie jest ograniczona). Każdy serwer zdefiniowany jest w ramach znacznika <server> w którym znajdować się powinny następujące informacje w poszczególnych znacznikach:
The configuration file is saved in the XML format. The main node of the file is <servers>; it contains definitions of Z39.50 servers (the number of the servers is not limited). Every server is defined within the <server> tag; the tag should contain the following information, in specific tags:
<name>– this is the server name which is displayed to the editor in the metadata search window; it can be entered for a particular language by using attributelangin the<name>tag; the value of attributelangshould be the two-letter symbol of the language (in accordance with the ISO 639 standard) in which the server name is specified; the default server name is determined in the<name>tag which does not have thelangattribute; Please note that particular names are defined in separate<name>tags.<host>– the Internet address of the Z39.50 server (the Internet Protocol address or domain address).<port>– the port of the Z39.50 server;<user>– the name of the user if the server requires authentication;<password>– the password of the user if the server requires it for authentication;<databases>– this tag contains the names of the databases which can be searched by the editor; particular names should be entered in<databases>tags;<recordencoding>–<name>- jest to nazwa serwera wyświetlana redaktorowi w oknie wyszukiwania metadanych. Nazwę można wprowadzić dla konkretnego języka poprzez zastosowanie w znaczniku<name>atrybutulang. Wartością atrybutulangpowinien być dwuliterowy symbol języka (zgodnie ze standardem ISO 639), w którym specyfikowana jest nazwa serwera. Domyślna nazwa serwera określana jest w znaczniku<name>, który nie posiada atrybutulang. Proszę zauważyć, że poszczególne nazwy definiowane są w odrębnych znacznikach<name>.<host>- jest to adres internetowy serwera Z39.50 (adres IP lub adres domenowy).<port>- jest to port serwera Z39.50.<user>- nazwa użytkownika, jeśli serwer wymaga uwierzytelniania<password>- hasło użytkownika, jeśli serwer wymaga go do uwierzytelniania<databases>- w tym znaczniku znajdują się nazwy baz danych, które redaktor może przeszukiwać. Poszczególne nazwy powinny być wprowadzane w znacznikach<database>.<recordencoding>- jest to kodowanie rekordów metadanych, które udostępnia definiowany serwer Z39.50.<queryencoding>– the encoding in which the phrases are to be sent to the server; the tag is optional; by default, the US-ANSI encoding is used;<setname>– the name of the set of properties which is to be returned fro every found element; this is an optional tag which, by default, assumes value F (from the word “full”); Value B (from “brief” is also often used; if the name of the set is not set correctly, the data retrieval will end in an error and the following message will appear in the Java console - jest to kodowanie, w jakim mają być wysyłane frazy w zapytaniach do serwera. Znacznik jest opcjonalny, domyślnie stosowane jest kodowanie US-ANSI.<setname>- jest to nazwa zbioru właściwości, który ma być zwrócony dla każdego znalezionego elementu. Jest to znacznik opcjonalny, domyślnie przyjmuje wartośćF(od full - pełen zbiór). Często jest też używana wartośćB(od brief - skrócone). Jeśli nazwa zbioru nie jest poprawnie ustawiona, pobieranie danych zakończy się błędem, a w konsoli Java pojawi się komunikat:Z3950SearchTask- Non surrogate diagnostics [25].;<queries>- jest to węzeł w którym definiuje się informacje związane z panelem wyszukiwawczym. Wszystkie wartości, które rozpoczynają się od znaku@związane są z językiem zapytań stosowanym w bibliotece JZKit 2 – the node in which information related to the search panel is defined; all values which begin with character @ are related to the query language used in the JZKit 2 library (http://jzkit.org/). I tak; thus:<attrset>- określa zestaw atrybutów jaki jest używany do wyszukiwania.<operator>- określa operator logiczny, który będzie używany do łączenia specyfikowanych wartości/fraz w polach wyszukiwawczych.<query>- specyfikuje nazwę atrybutu po którym możliwe będzie wyszukiwanie oraz zapytanie wyszukiwawcze związane z tym atrybutem. Nazwa atrybutu podobnie jak w przypadku nazwy serwera może być wprowadzona w wielu językach (użycie atrybutulang). Domyślna nazwa atrybutu to wartość zawarta w znaczniku<name>, który nie posiada atrybutu lang. Zapytanie wyszukiwawcze specyfikuje się w znaczniku<searchquery>, gdzie w miejsce znacznika$1wstawiana jest wartość z odpowiedniego pola wyszukiwawczego.
...
- – defines the attribute set used for searching;
<operator>– determines the logical connective which will be used for connecting the values/phrases specified in the search fields;<query>– specifies the name of the attribute for searching and the search query related to that attribute; the attribute name, just like the server name, can be entered in many languages (with the use of the lang attribute); the default attribute name is the value in the <name> tag which does not have the lang attribute; the search query is specified in the<searchquery>tag where the $l tag is replaced with the value from the appropriate search query.
In order to change the configuration of the Z39.50 extension, the user should follow the instructions included in the application configuration section.